Our Treatments
LASIK Surgery
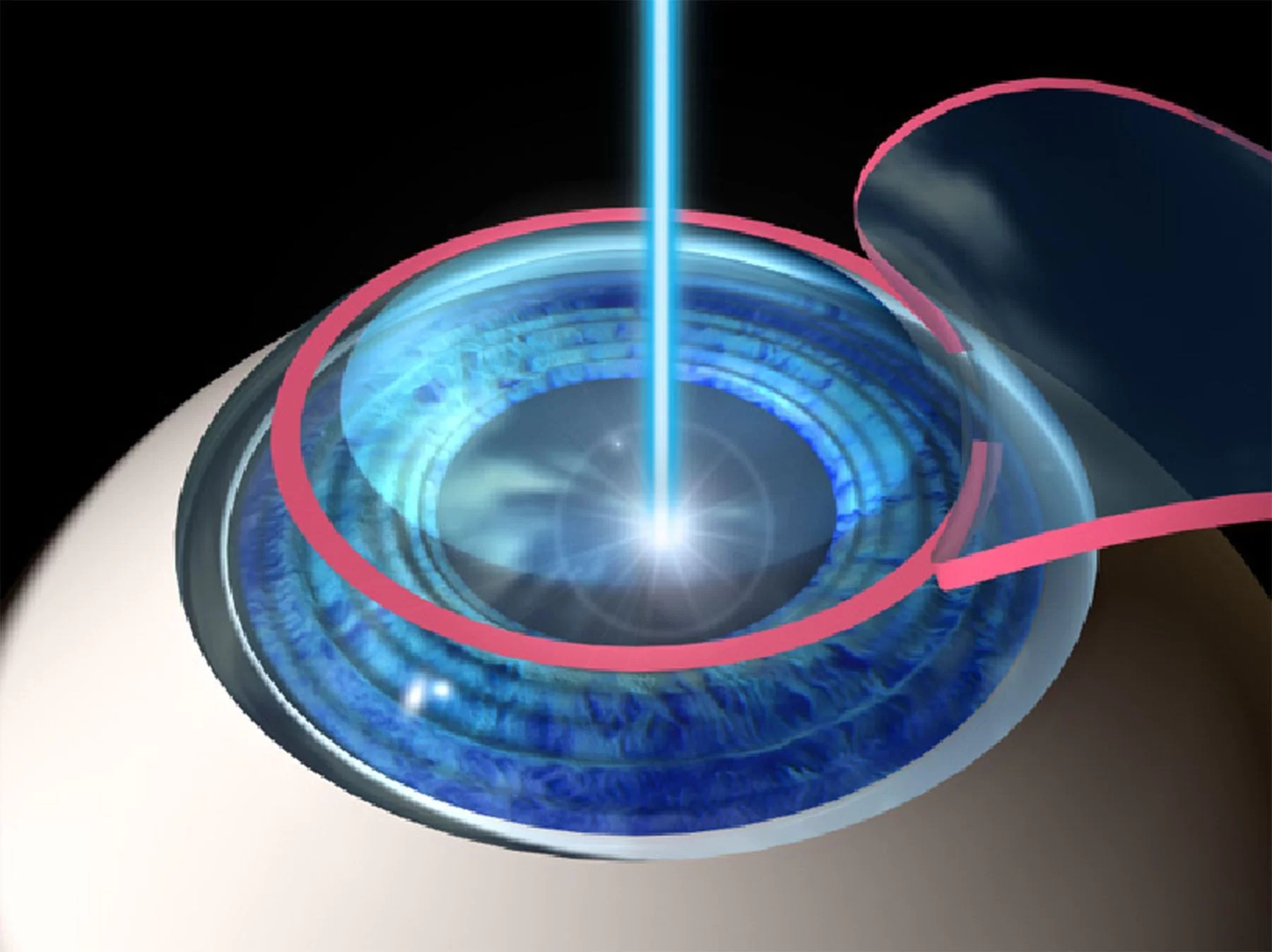
LASIK Surgery (Keratomileusis in situ) is the safest and most accurate for the correction of myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism. For this procedure, the surgeon uses an instrument, called a microkeratome, to create a thin sheet of corneal tissue (flap). This flap is raised and the laser is used to remove a thin layer of tissue from the surface of the exposed cornea. At the end of the treatment, the flap is repositioned and adheres to the cornea without the need for sutures. The surgery is ambulatory, is performed with topical anesthesia (with drops of anesthetic eye drops) and lasts a few minutes.
Visual recovery is usually very fast (some days) and the discomfort is limited to the first hours after surgery.
When the visual defect is very high, the cornea is very thin or its curvature has extreme values, it is preferable to perform other types of surgeries, such as intraocular lens implant.
Cataract Surgery
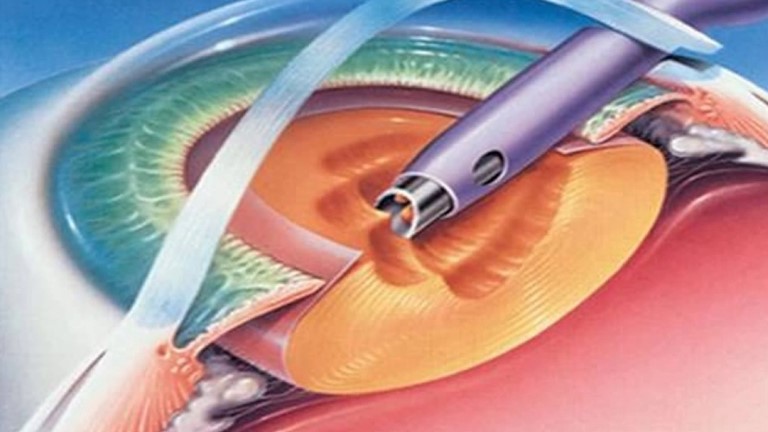
Cataract means the opacification of the lens. The surgery involves removing the lens and replacing it with an intraocular lens. The surgery is performed on an outpatient basis, with local anesthesia (injection of anesthetic in the periocular region) or topical (drops of anesthetic eye drops).
A microincision (2.4 mm) is made at the periphery of the cornea through which a small probe is inserted. This probe is inserted into the interior of the lens sac and, through the emission of ultrasound, aspirates its contents. Once this sack is cleaned, and through the same incision, the intraocular lens is injected. The power of the inserted lens also allows to compensate any pre-existing refractive errors (myopia, hyperopia). Being a microincision, it is not necessary to put stitches.
Visual recovery is usually very fast (some days) and the discomfort is limited to the first hours after surgery.
Presbyopia Surgery
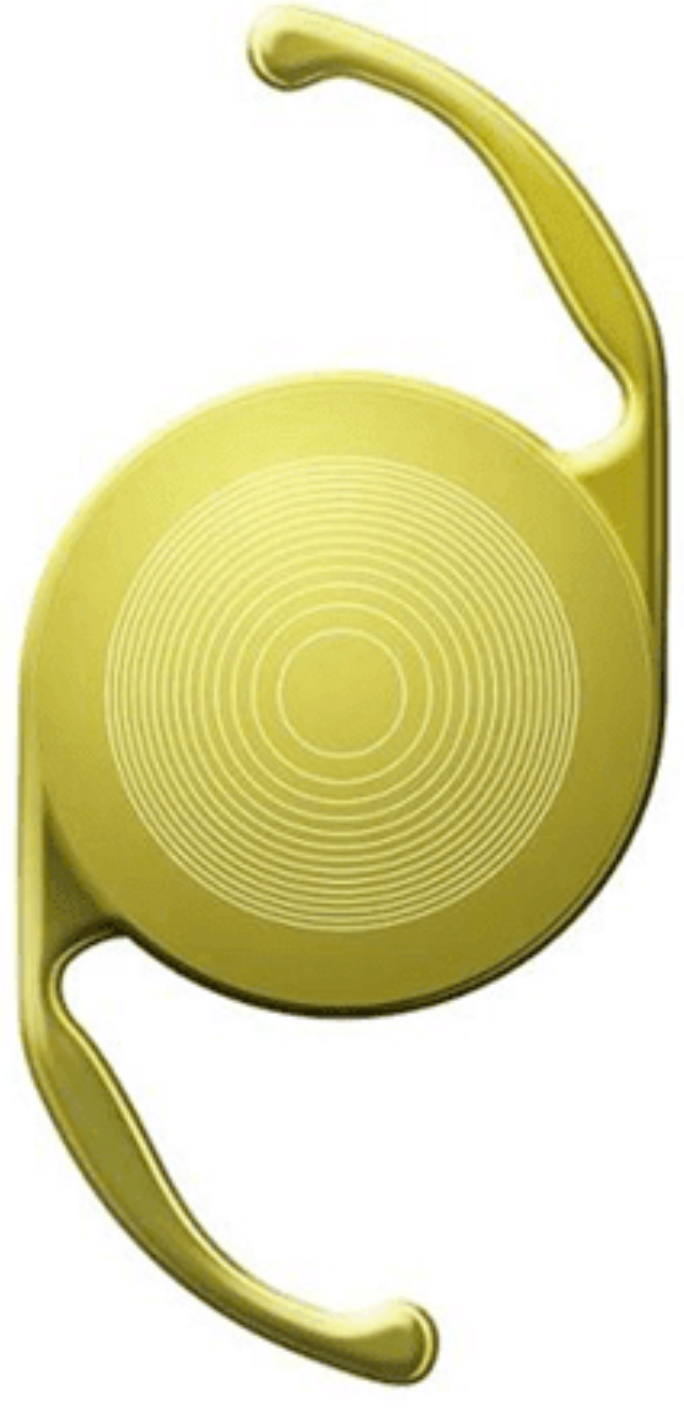
Surgery of the presbyopia is identical to cataract surgery, but using a Multifocal Intraocular Lens, which allows to improve near vision. The surgery is performed on an outpatient basis, with local anesthesia (injection of anesthetic in the periocular region) or topical (drops of anesthetic eye drops).
A microincision (2.4 mm) is made at the periphery of the cornea through which a small probe is inserted. This probe is inserted into the interior of the lens sac and, through the emission of ultrasound, aspirates its contents. Once this sack is cleaned, and through the same incision, the intraocular lens is injected.
Being a microincision, it is not necessary to put stitches. Visual recovery is usually very fast (some days) and the discomfort is limited to the first hours after surgery.

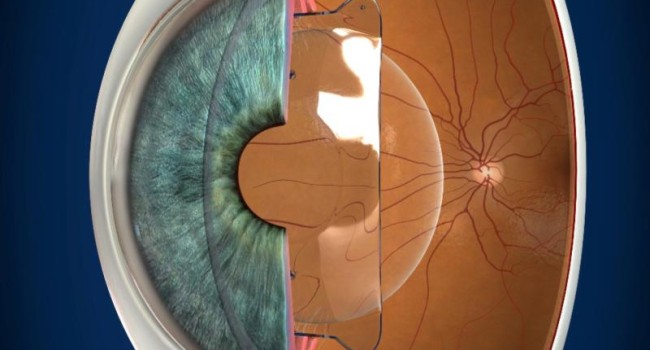
Intraocular lens surgery
When the visual defects are very high or the very thin cornea is not possible to perform a laser surgery , in these cases the solution consists of implanting an intraocular lens in front of the lens. This surgery is recommended for people under 50 who have a clear lens with a good accommodation capacity. The surgery is performed on an outpatient basis, with local anesthesia (injection of anesthetic in the periocular region) or topical (drops of anesthetic eye drops). A microincision (3.0 mm) is made at the periphery of the cornea through which the intraocular lens is injected. Once inside the eye, the lens is positioned in the posterior chamber, between the iris and the lens. Being a microincision, it is not necessary to put stitches. Visual recovery is usually very fast (some days) and the discomfort is limited to the first hours after surgery.
